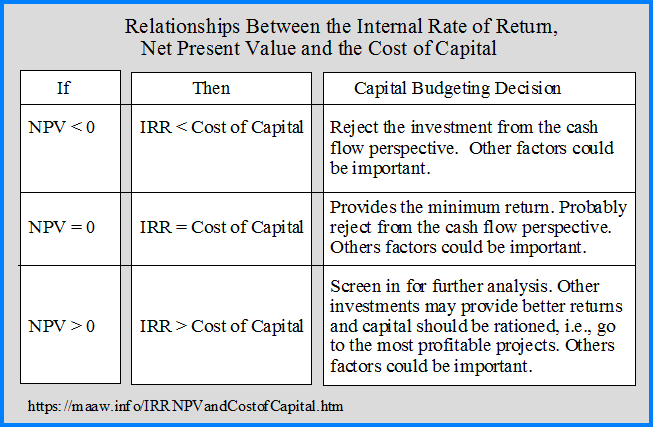
11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. The entire equation is set up with the knowledge that at the IRR, NPV is equal to zero.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
Essentially, IRR solves for the discount rate that sets the NPV equation to zero. This comprehensive guide explores internal rate of return vs net present value, shedding light on when and how to apply each method effectively. Investment decisions are crucial to the success of any financial endeavor, and the use of appropriate evaluation techniques is essential for informed decision-making.
What is IRR?
For instance, a real estate investor might pursue a project with a 25% IRR if comparable alternative real estate investments offer a return of, say, 20% or lower. However, this comparison assumes that the riskiness and effort involved in making these difficult investments are roughly the same. If the investor can obtain a slightly lower IRR from a project that is considerably less risky or time-consuming, then they might happily accept that lower-IRR project. In general, though, a higher IRR is better than a lower one, all else being equal. So, JKL Media’s project has a positive NPV, but from a business perspective, the firm should also know what rate of return will be generated by this investment. To do this, the firm would simply recalculate the NPV equation, this time setting the NPV factor to zero, and solve for the now unknown discount rate.
- NPV is an absolute measure of the difference between the present value of cash inflows and the present value of cash outflows over a specific period of time.
- Investment decisions are crucial to the success of any financial endeavor, and the use of appropriate evaluation techniques is essential for informed decision-making.
- Similarly, the two methods, considers all cash flows over the life of the project.
- However, IRR cannot be entirely disregarded, as it remains one of the most widely used metrics in corporate finance.
IRR Calculation Example
When calculated, IRR represents an annualized rate of growth that an investment is expected to achieve. Conversely, if the IRR on a project or investment is lower than the cost of capital, then the best course of action may be to reject it. Overall, while there are some limitations to IRR, it is an industry standard for analyzing capital budgeting projects.
What Is IRR?
IRR can be useful, however, when comparing projects of equal risk, rather than as a fixed return projection. NPV or otherwise known as Net Present Value method, reckons the present value of the flow of cash, of an investment project, that uses the cost of capital as a discounting rate. On the other hand, IRR, i.e. internal rate of return is a rate of interest which matches present value of future cash flows with the initial capital outflow. The IRR is the discount rate at which the net present value (NPV) of future cash flows from an investment is equal to zero.
However, ROI is not necessarily the most helpful for lengthy time frames. It also has limitations in capital budgeting, where the focus is often on periodic cash flows and returns. IRR differs in that it involves multiple periodic cash flows—reflecting that cash inflows and outflows often constantly occur when it comes to investments.
However, in the case of two mutually exclusive projects, the decision rules will sometimes draw different conclusions. For example, project X might have a larger NPV than project Y, but project Y might have a larger IRR. This conflict child tax credit 2021 usually stems from differences in the cash flows of the two projects, which leads to a different ranking between the NPV and IRR. Whenever this conflict arises, the NPV, not the IRR, should be used to select the project to invest in.
The internal rate of return (IRR) is the discount rate that makes the net present value (NPV) of all cash flows from a particular project equal to zero. For a project with one initial outlay, the IRR is the discount rate that makes the present value of the future after-tax cash flows equal to the investment outlay. If rates of return vary over the life of the project, an NPV analysis can accommodate these changes. The NPV model also works better when the discount rate isn’t known, and as long as a project’s NPV is greater than zero, the project is considered financially viable. It can be misconstrued or misinterpreted if used outside of appropriate scenarios.
Another circumstance that may cause mutually exclusive projects to be ranked differently according to NPV and IRR criteria is the scale or size of the project. In many respects, NPV is considered a superior metric to IRR because it directly reflects the net value added to the firm. However, IRR cannot be entirely disregarded, as it remains one of the most widely used metrics in corporate finance. Yes, this situation can occur when a project’s cost of capital exceeds the IRR. While both methods offer their own advantages and insights into the value of investment projects, they also have their respective limitations and areas where they best apply. They also aim to provide a perspective on the potential return of an investment project.

Comentarios recientes